What is Docker?
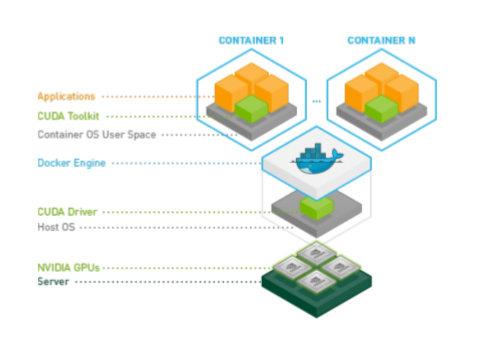
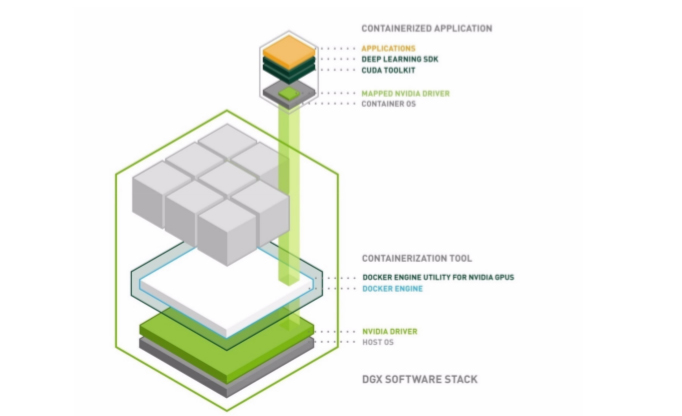
A Docker container is a mechanism for bundling a Linux application with all of its libraries, data files, and environment variables so that the execution environment is always the same, on whatever Linux system it runs and between instances on the same host. Docker containers are user-mode only, so all kernel calls from the container are handled by the host system kernel.
Docker containers wrap a piece of software in a complete filesystem that contains everything needed to run: code, runtime, system tools, system libraries - anything that can be installed on a server. This guarantees that the software will always run the same, regardless of its environment.
Docker provides both hardware and software encapsulation by allowing multiple containers to run on the same system at the same time each with their own set of resources (CPU, memory, etc) and their own dedicated set of dependencies (library version, environment variables, etc.). Docker also provides portable Linux deployment: Docker containers can be run on any Linux system with kernel is 3.10 or later. All major Linux distros have supported Docker since 2014. Encapsulation and portable deployment are valuable to both the developers creating and testing applications and the operations staff who run them in data centers.
Docker provides many more important features.
• Docker's powerful command-line tool, 'docker build', creates Docker images from source code and binaries, using the description provided in a "Dockerfile".
• Docker's component architecture allows one container image to be used as a base for other containers.
• Docker provides automatic versioning and labeling of containers, with optimized assembly and deployment. Docker images are assembled from versioned layers so that only the layers missing on a server need to be downloaded.
• Docker Hub is a service that makes it easy to share docker images publicly or privately.
• Containers can be constrained to a limited set of resources on a system (e.g one CPU core and 1GBof memory).
Docker provides a layered file system that conserves disk space and forms the basis for extensible containers.